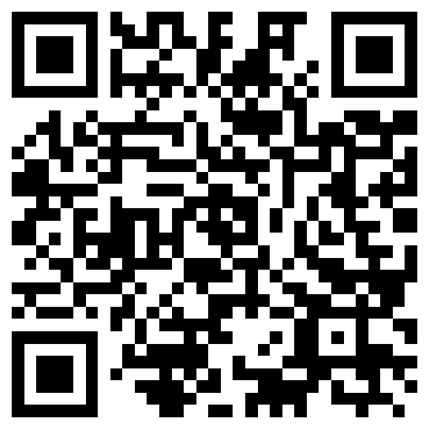
The difference between a 5/2 way and a five/3 way solenoid valve lies in their positions, capability, and packages. here's an in depth contrast:
1. variety of Positions
five/2 manner Valve:
Has 2 positions.
The valve switches among two states, directing airflow to both of the 2 actuator ports.
5/3 way Valve:
Has 3 positions.
the additional middle function permits for extra complicated manage over the pneumatic machine.
2. capability
five/2 manner Valve:
Directs compressed air alternately to 2 outlets (e.g., a double-performing cylinder).
in one role, air flows to port A (extending the cylinder), and port B is exhausted.
within the different role, air flows to port B (retracting the cylinder), and port A is exhausted.
five/3 way Valve:
gives three wonderful modes:
middle function: Can provide one of the following configurations:
All ports blocked: Holds the actuator in its modern function through blockading all airflow.
center exhaust: Vents each actuator ports (A and B) to allow unfastened movement or depressurization.
middle pressurization: elements air to each actuator ports to lock the actuator in a neutral function.
end positions: characteristic like a 5/2 way valve, alternating air between ports A and B.
three. applications
five/2 way Valve:
ideal for simple actuation responsibilities which includes running double-acting cylinders or directional control in automation.
commonplace in structures wherein handiest two states (extend and retract) are needed.
5/3 manner Valve:
Used for extra advanced control wherein the actuator ought to:
Pause in a specific function (e.g., with all ports blocked).
pass freely without air strain (e.g., center exhaust).
Be locked with equal strain on each sides (e.g., center pressurization).
suitable for packages requiring finer manage, inclusive of function holding or protection stop situations.
four. Actuation
each sorts can be controlled the usage of solenoids, but a five/3 manner valve requires extra manage common sense or solenoid pairs to manipulate the center role.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 5/2 Way Valve | 5/3 Way Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Positions | 2 | 3 |
| Middle State | None | All ports blocked, center exhaust, or center pressurization |
| Use Case | Simple actuation | Advanced control and position holding |
| Control | 2 solenoids or 1 solenoid with spring | 2 or 3 solenoids depending on design |
Each type serves a specific purpose, with the 5/3 way valve offering greater flexibility at the cost of increased complexity.