The reasons why pneumatic cylinders are prone to failure

1. Poor material quality
Pneumatic cylinders need to withstand considerable impact, vibration and load during operation. If the material quality is poor, they are prone to damage such as cracks and fatigue. Therefore, when purchasing and using pneumatic cylinders, it is essential to pay attention to the quality of the materials, especially the piston rods and cylinder barrels of the cylinders, to ensure their service life.
Second, improper operation
Improper operation is also one of the reasons why pneumatic cylinders are prone to failure. During the operation process, if it is not carried out in the correct way and sequence, it will affect the usage effect of the cylinder and even lead to its damage. For instance, when reversing the air line, the operator changed the direction frantically without stopping to reduce the air pressure, which caused the cylinder piston to collide and get damaged.
Iii. Dust, dirt, etc
Due to the complex on-site environment, it is inevitable that the work will be disturbed by impurities such as dust and dirt, which will in turn affect the normal operation of the cylinder. These impurities may adhere to the sealing parts, sliding parts, cylinder block, cylinder head and other areas of the cylinder, hindering the normal use of the cylinder and thus accelerating its wear.
How can we prevent the occurrence of faults in pneumatic cylinders? The following points need to be noted:
1. Select high-quality cylinders;
2. When debugging the gas path, it is necessary to follow the correct steps and methods.
3. Keep the site clean and hygienic, and try to avoid impurities from entering the cylinder.
4. Do a good job in the maintenance of the cylinder, and regularly inspect and replace the sealing parts and dynamic sealing components of the cylinder.
To sum up, the main reasons why pneumatic cylinders are prone to failure are poor material quality, improper operation, as well as dust and dirt. To avoid the occurrence of cylinder failures, we need to enhance our attention in aspects such as selection, operation and maintenance.
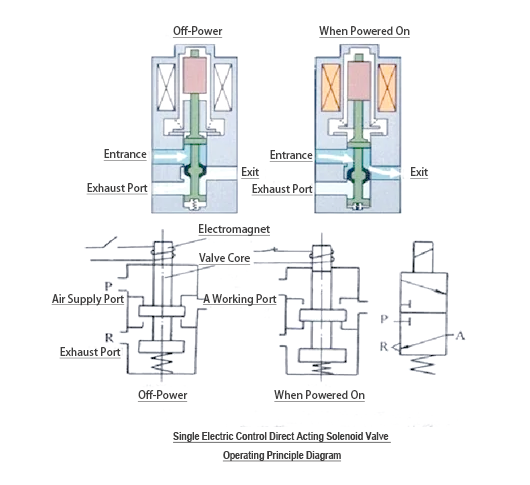
The working principle of the cylinder and the troubleshooting of solenoid valves
There are various types of cylinders, among which one type is widely used because of its good stroke control. This type of cylinder is used in conjunction with pneumatic solenoid valves to achieve the ejection and retraction of the cylinder through air intake and exhaust.
When the cylinder is pushed out, air enters from the bottom and exhausts from the top. When retracted, it takes in air from the top and exhausts from the bottom. The P port of the pneumatic solenoid valve is the air inlet, the A and B ports are the air outlets connected to the cylinder, and the R and S ports are the exhaust ports, which are usually not connected.
It is very simple to determine whether the pneumatic solenoid valve is damaged. Just press the manual button. If the cylinder operates, the solenoid valve is normal. If it doesn't move, it might be a circuit problem or a malfunction of the solenoid valve itself. There is usually an indicator light on the pneumatic solenoid valve. If it does not light up, it indicates that there is no power supply. When checking the circuit or replacing it, pay attention to whether the voltage matches.