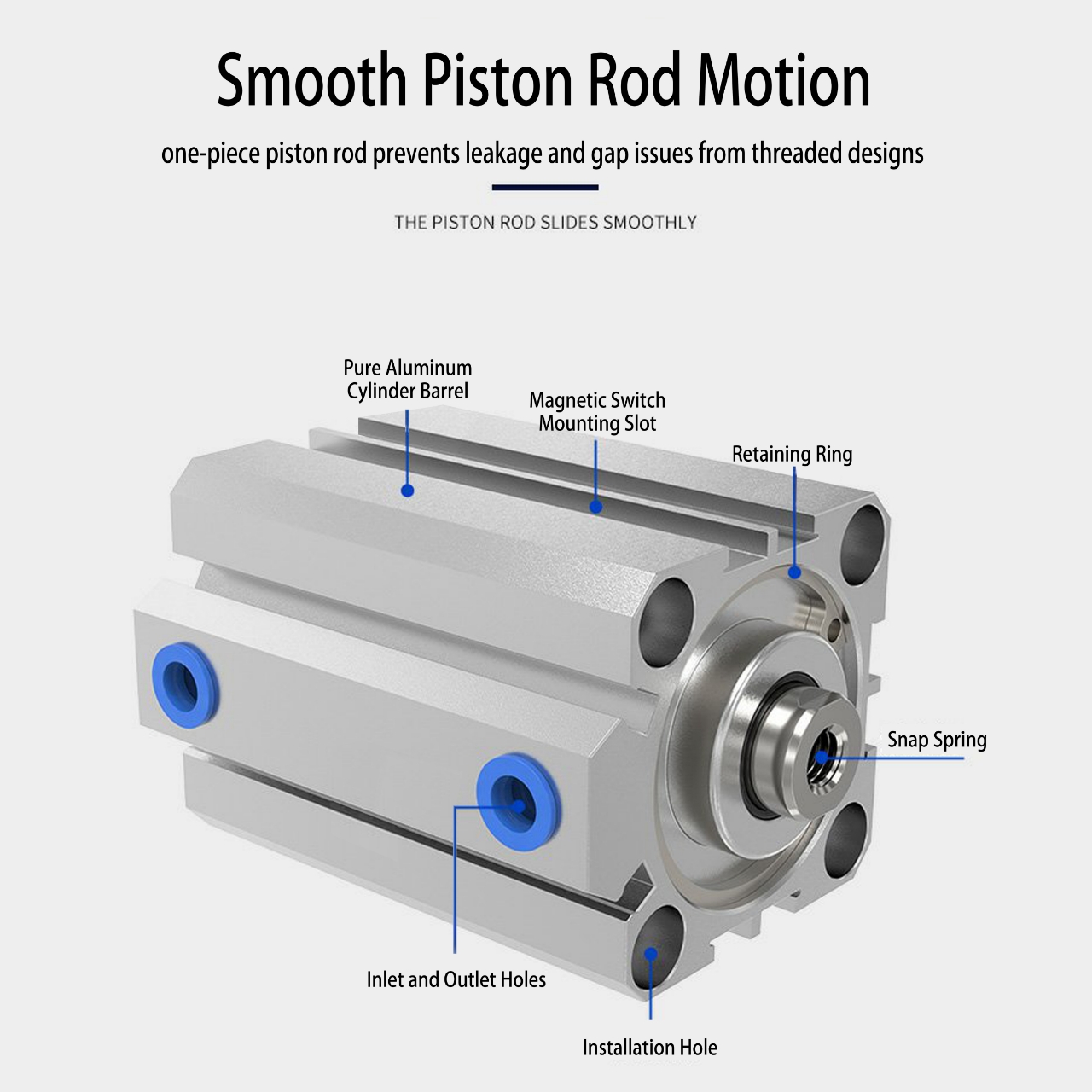
The terms air valve and air solenoid talk over with exclusive components used in pneumatic systems, and whilst they're associated in some programs, they serve awesome functions. right here’s a breakdown of the differences:
1. Air Valve:
An air valve is a device used to control the flow of compressed air in a pneumatic system. It regulates the path, pressure, and go with the flow rate of air to diverse additives consisting of cylinders, actuators, or gear. Air valves are available many types, such as guide, pneumatic, and solenoid-operated variations.
varieties of Air Valves:
guide Valves: operated by hand (e.g., a lever or knob).
Pneumatic Valves: Operated through air pressure (e.g., pilot-operated valves).
Solenoid Valves: Operated by way of an electric powered signal (more on this under).
features of Air Valves:
Controlling Airflow: Regulates whether or not air is allowed to flow or no longer and can also change the path of glide.
Shutting Off Air: Stops the air deliver to a component or tool.
Regulating stress: a few air valves can also control or modify the pressure within a system.
2. Air Solenoid:
An air solenoid is specially an electromagnetic tool this is used to control air valves (typically solenoid-operated air valves). The solenoid acts as the actuator that opens, closes, or shifts the valve mechanism in reaction to an electric powered sign.
In different phrases, an air solenoid isn't a valve with the aid of itself but a issue that is used to govern a valve's operation remotely using electric alerts.
the way it Works:
Electromagnetic Actuation: A solenoid is largely a coil of cord that, whilst energized with electric modern, creates a magnetic discipline. This discipline movements a plunger or armature within the solenoid.
control of the Valve: The motion of the solenoid's plunger without delay controls the valve mechanism (along with a spool, diaphragm, or poppet) interior a solenoid valve, figuring out whether the air is permitted to float via or be diverted to another port.
commonplace kinds of Air Solenoids:
2-manner Solenoid: Controls a easy on/off characteristic.
3-manner Solenoid: Directs the air float to considered one of paths (normally used for unmarried-performing cylinders).
four-manner Solenoid: Controls more complicated capabilities, including switching air to extend or retract a double-acting cylinder.
Key differences:
| Feature | Air Valve | Air Solenoid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A device that regulates the flow of air in a pneumatic system | An electromagnetic actuator used to control the movement of a valve |
| Primary Function | Controls the direction, flow, and pressure of air | Provides the electric control signal to actuate the valve |
| Operation | Can be manually, pneumatically, or electrically operated | Operates when an electrical current activates the solenoid coil |
| Types | Manual valves, pneumatic valves, solenoid valves | Solenoid actuators that control air valves (e.g., 2-way, 3-way, 4-way) |
| Use in a System | Directly controls air flow and pressure in the system | Controls a valve’s movement based on electrical signals |
| Control Type | Manual, pneumatic, or electrical | Electrical (solenoid) |
Example of Integration:
In a solenoid valve, the solenoid is the component that controls the valve's operation. For example, when the solenoid is energized (with an electric signal), it moves a plunger inside the valve to allow or block airflow through the valve. So, the air valve (the solenoid valve) uses an air solenoid to control the flow of air within a system.
Summary:
- Air Valve: The component that controls the airflow, pressure, and direction of air in a pneumatic system.
- Air Solenoid: An electromagnetic actuator used to control an air valve via electrical signals, typically used in solenoid-operated valves.
So, while air valves control airflow directly, air solenoids are used to operate those valves remotely through electrical signals.