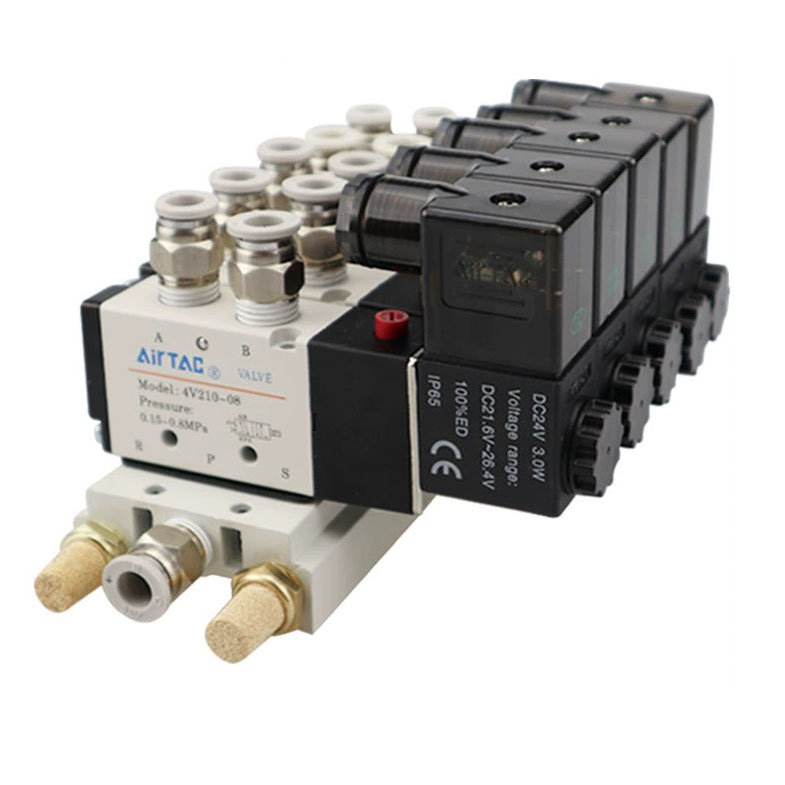
A 5/2 manner solenoid valve is generally used to govern air or fluid go with the flow in pneumatic or hydraulic structures. It has five ports and positions (consequently the call 5/2), and it's far on the whole used to control double-performing cylinders. right here's the way it works:
components:
Ports (5 in overall):
P (pressure port): The inlet for pressurized air or fluid.
A (working port A): one of the two ports related to the cylinder.
B (working port B): the alternative port connected to the cylinder.
EXH1 (Exhaust port 1): Exhaust for port A.
EXH2 (Exhaust port 2): Exhaust for port B.
Coils: There are usually two solenoids (electromagnetic coils) that control the valve's moving. every solenoid is activated or deactivated to transport the valve's internal spool among positions.
Operation:
The valve has main positions:
function 1 (usually Closed):
The P (strain port) is connected to A (working port A), and B (working port B) is hooked up to EXH2 (exhaust port 2).
This position generally extends the cylinder (pushes the piston in the double-appearing cylinder).
function 2 (Shifted position):
The P (strain port) is hooked up to B (working port B), and A (working port A) is connected to EXH1 (exhaust port 1).
This function commonly retracts the cylinder (pulls the piston returned).
the way it works:
when the solenoid coil is energized, it shifts the internal valve spool from role 1 to put 2 (or vice versa).
In position 1, pressurized air or fluid flows into port A to extend the actuator, at the same time as port B is exhausted.
In role 2, the pressurized air or fluid flows into port B to retract the actuator, whilst port A is exhausted.
precis:
The 5/2 manner solenoid valve lets in you to manipulate the path of go with the flow in a double-performing cylinder or actuator, shifting the valve to exchange among positions (expand and retract) based totally on solenoid activation. It’s called "5/2" because it has 5 ports and two possible states (positions).